REVOLUTIONARY AI FROM UGM COULD CHANGE THE FIGHT AGAINST TUBERCULOSIS—HERE'S HOW
Cutting-Edge Technology to Speed Up Diagnosis and Expand Healthcare Access
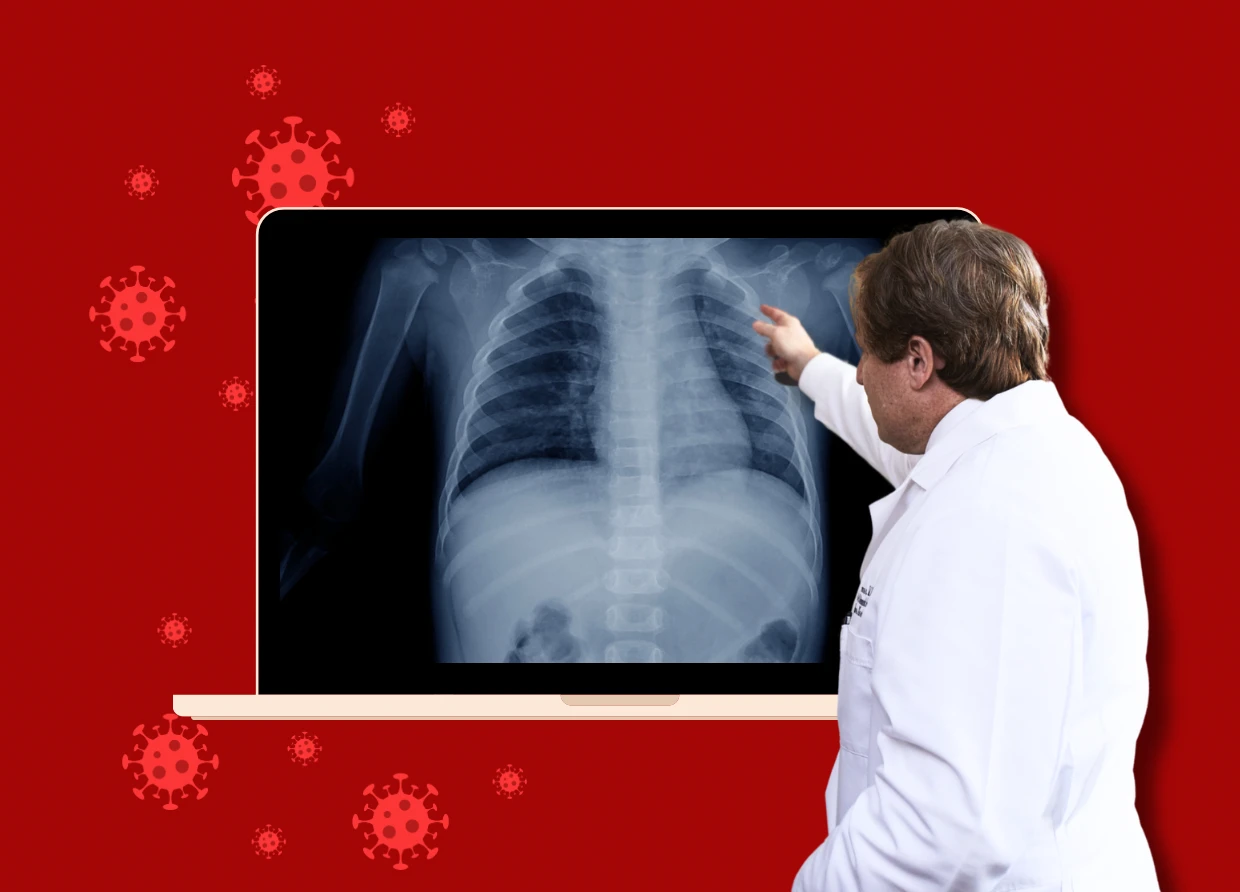
The battle against tuberculosis (TB) in Indonesia is entering a new era, thanks to groundbreaking artificial intelligence (AI) research by Universitas Gadjah Mada (UGM). A team of researchers has developed an innovative computer-aided detection (CAD) software designed to enhance the speed and accuracy of TB screening. This technology could be a game-changer for healthcare professionals, especially in remote areas where medical resources are scarce.
But this innovation is not just about speed—it’s about equity. The UGM research team is determined to ensure that vulnerable groups, including women, children, and people with disabilities, have better access to TB diagnosis and treatment.
The Urgent Need for a Breakthrough
With Indonesia ranking second globally in TB cases, the country faces an uphill battle in detecting and treating this deadly disease. Of the estimated 1.06 million TB cases in Indonesia, only around 81 percent have been diagnosed, far from the 100 percent target set by the World Health Organization (WHO). Delays in diagnosis often lead to more severe complications, increased transmission, and higher mortality rates.
By utilizing AI-powered CAD software, healthcare workers can analyze chest X-rays more effectively, reducing reliance on imported technology and addressing Indonesia’s pressing TB crisis head-on.
Bringing Healthcare to the Most Vulnerable
One of the biggest obstacles to TB elimination in Indonesia is ensuring access to proper screening and treatment for marginalized communities. Many women in rural areas struggle to seek medical care due to societal norms, while people with disabilities often face physical and social barriers to accessing healthcare services.
The new AI-assisted screening tool developed by UGM is expected to bridge this gap, allowing faster and more reliable detection of TB cases in underserved regions. With this technology, even health workers in remote areas with minimal medical training can conduct preliminary screenings, ensuring that more people receive the care they need.
A Step Towards Nationwide Implementation
The Indonesian Ministry of Health has already taken significant steps toward active case finding (ACF) in 25 cities and districts, leading to a 2-7 percent increase in TB detection in 2024. However, the real challenge lies in expanding this initiative to more remote and hard-to-reach areas.
UGM’s AI-driven technology could be the key to scaling up TB detection efforts nationwide. The research team is optimistic that, with the right policies and technological integration, Indonesia can significantly accelerate its fight against TB.
Global Collaboration for a Healthier Indonesia
The development of this AI-powered TB detection tool is not a solo effort. UGM is collaborating with leading institutions such as the University of Melbourne, Monash University Indonesia, Universitas Sebelas Maret, and advocacy organizations like the Papua Health and Community Development Foundation (YPKMP) and the Center for Advocacy for Women, Disabilities, and Children (SAPDA).
Additionally, the project has gained support from Australia’s Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade (DFAT) through the KONEKSI program, highlighting the international commitment to tackling TB in Indonesia.
The Future of TB Detection: A Race Against Time
With this AI innovation, UGM is not just developing new technology—it is revolutionizing how Indonesia approaches TB elimination. The potential to diagnose TB faster, more accurately, and in more regions could bring the country closer to its goal of eradicating the disease.
Could this breakthrough finally turn the tide in Indonesia’s fight against tuberculosis? The next few years will determine whether AI-powered healthcare can truly transform lives. One thing is certain: the battle is far from over, but with technology on our side, victory may be within reach.
#THE S MEDIA #Media Milenial #AI-powered TB detection #tuberculosis screening technology #Universitas Gadjah Mada research #CAD software for healthcare #artificial intelligence in medicine #tuberculosis elimination in Indonesia #healthcare accessibility #remote medical diagnosis #Ministry of Health initiatives #global collaboration in TB research #AI innovation in healthcare #early disease detection #medical technology advancements #public health solutions #equitable healthcare access